Raid Configuration Tool Ibm
RAID configuration on the IBM Power platform RAID stands for Redundant Array of Independent Disks and it involves two key design goals: Increased data reliability and increased input/output (I/O) performance. When multiple physical disks are set up to use the RAID technology, they are said to be in a RAID array.
This array distributes data across multiple disks, but the array is seen by the computer user and operating system as one single disk. RAID can be set up to serve several different purposes.
Lenovo offers a suite of management tools to simplify the configuration and management of the RAID controllers for ThinkSystem, ThinkServer, and System x servers.
Different types of RAID levels Different types of RAID levels are available. Some are basic RAID levels and some are a combination of basic levels.
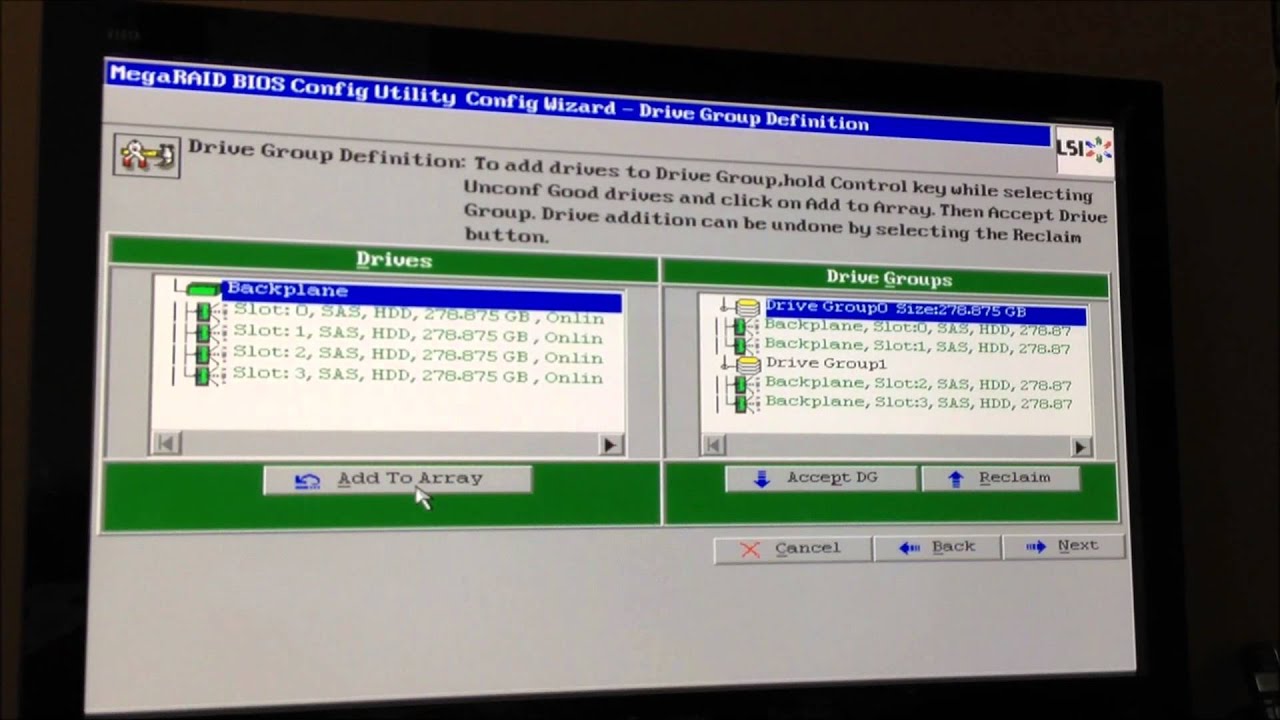
Types Of Raid Configuration
RAID 0. RAID 1. RAID 5. RAID 6. RAID 10. RAID 50. RAID 60 Here, RAID 0, RAID 1, and RAID 5 are the basic RAID levels and the remaining RAID 6, RAID 10, RAID 50, and RAID 60 are the combination of the basic RAID levels.
Each RAID level is defined for a specific purpose. Read through the following table to get a better understanding about the various RAID levels.


Disk Arrays or RAIDs are a widely accepted I/O system architecture, useful for a wide range of applications. Before a RAID can be used, one needs to configure the RAID to select parameters such as the RAID level to use, the stripe unit to use, how large of a cache to use, and so on. Selecting these configuration parameters can be quite complex, yet no aids are available today to help the user configure his RAID. The optimal selection of the parameters strongly depends on the specific workload characteristics of the application.
In this paper, we describe a configuration tool called Raidtool which is intended to support the systems designer in the selection of the configuration parameters. Our approach consists of three basic steps. The first step is to collect a trace of I/Os while running one or more typical applications. In the second step, this trace data is analyzed to determine the workload characteristics of the applications. In the third and final step, we use a simulator to evaluate the different RAID controller configurations.